Last update: November 6, 2025
11 minute read
Iron Deficiency Symptoms: What Are the Early Warning Signs and How to Address Them?
Discover the early signs of iron deficiency, understand its impact on health, and explore dietary and supplement solutions to improve iron levels.

By Derick Rodriguez, Associate Editor
Edited by Dr. Dimitar Marinov, MD, RDN, PhD

Iron deficiency is an often overlooked but critical issue that can silently sap your energy and vitality. When your body lacks enough iron, it can lead to serious health concerns like anemia, making everyday activities feel monumental.
Understanding how to identify the signs and what dietary choices and supplements, like VitaRx Iron, can help is essential for maintaining your overall health and well-being.
Key takeaways
- Iron deficiency can happen before anemia develops, with early symptoms often being silent
- Low iron affects your body's oxygen delivery, leading to fatigue and reduced exercise tolerance
- Dietary sources rich in heme and non-heme iron can help maintain adequate iron levels
What is iron deficiency?
It’s when your body doesn’t have enough iron to build adequate hemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying protein in red blood cells, so tissues don’t get the oxygen they need to perform. Early phases can be silent, then progress to iron-deficiency anemia with more obvious symptoms.
What actually causes iron to drop?
- Blood loss (heavy periods, GI bleeding, frequent blood donation), low intake, poor absorption (celiac, bariatric surgery, IBD), or higher needs (pregnancy, growth, endurance training).
- Spot and treat the cause while you replete iron—both matter for lasting results.
How iron works in the body
Iron is a core component of hemoglobin, moving oxygen from lungs to tissues and supporting energy production, concentration, and physical performance.
When iron is low, fatigue climbs and exercise tolerance drops; your engine is fine, but the fuel line is pinched. That’s why simple activities feel tougher.
In plain English, this means:
- Hemoglobin carries oxygen, ferritin stores iron, and transferrin moves it around; low ferritin often shows up first.
- Low iron → low hemoglobin → less oxygen to brain/muscle → fatigue, poor focus, lower workout capacity.
Anemia is more common than you think
An estimated ~1.62 billion people worldwide had anemia in 2008, and roughly half of anemia cases are attributed to iron deficiency (the proportion varies by population). That’s massive. Pagophagia (craving ice) is a specific form of pica that’s strongly associated with iron deficiency in clinical settings—if you chew ice often, flag it with your clinician
Think of it this way: The “ice fix” may briefly boost alertness, but it’s a red flag—resolving the iron deficit usually makes the craving fade.
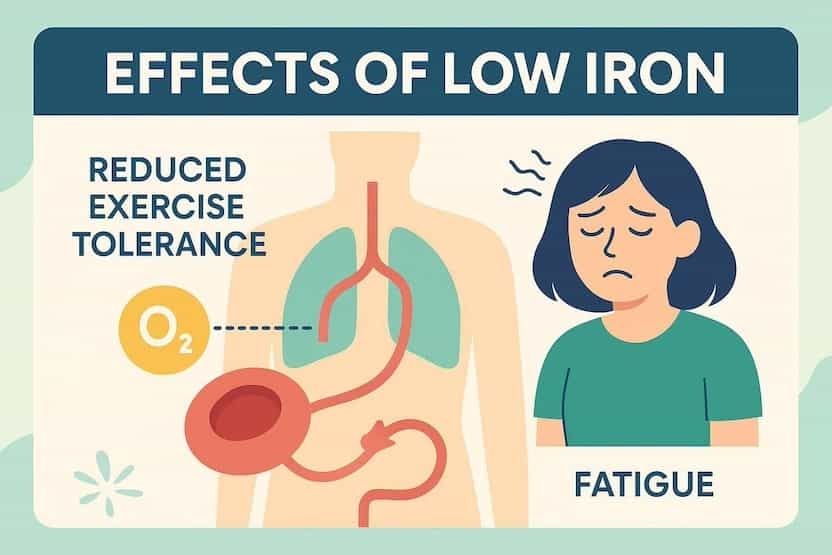
Recognizing the symptoms
Common iron deficiency symptoms include unexplained fatigue, weakness, pale or sallow skin, headaches, dizziness or lightheadedness, shortness of breath on exertion, cold hands and feet, and sometimes a rapid heartbeat.
Mild cases may show no symptoms, while more serious deficiency or anemia brings the classic trio: fatigue, pallor, and breathlessness. Subtle at first; louder over time.
Here’s why that matters: These overlap with thyroid issues, sleep apnea, B12/folate deficiency, and depression; labs help pinpoint the cause instead of guessing.
Mild or moderate iron-deficiency anemia may cause few or nonspecific symptoms; if it goes untreated, it is associated with adverse outcomes like complications in pregnancy and developmental delays in children—another reason to test when patterns continue.
Now that we’ve covered the basics, you might also be wondering about other tell-tale signs:
- Brittle or spoon-shaped nails, hair shedding, mouth sores/glossitis
- Restless legs (often worse at night), cold intolerance
- In kids: poor attention, delayed development—test early

Fatigue: More than just tiredness
This isn’t regular tired—it’s the kind that shrinks your day, saps motivation, and makes workouts feel like wading through wet concrete.
When hemoglobin dips, oxygen delivery to muscle and brain drops. Energy and focus follow. Work, training, parenting, it all feels heavier.
Here’s why that matters: Your heart rate rises for the same workload, recovery drags, and “mental fog” creeps in, classic low-oxygen effects.
Pale skin and its hidden clues
Paler skin or inside of the eyelids can be a clue to lower Red blood cell mass or hemoglobin, but this sign is neither sensitive nor specific. A quick look can prompt testing, but labs confirm the diagnosis. Small clues, big insights.
VitaRx Tip
Pull down your lower eyelid; if it’s very pale instead of rosy, iron may be low; spooned nails add to the clue list.
Shortness of breath: When every step counts
If stairs feel like a hike, it might be less about lung capacity and more about oxygen delivery. Low iron means less hemoglobin, so your heart and lungs compensate, and you feel winded. Every step starts to count.
But wait, does that mean it’s urgent? If you have chest pain, severe breathlessness, fainting, or symptoms in pregnancy/children, seek care promptly.
More serious cases may also bring chest pain, headache, or dizziness—signals to get checked promptly.
It's everywhere!
Iron-deficiency anemia is the most common type of anemia worldwide, affecting people across ages and life stages.
Dietary sources and the role of supplements
Food first, always. You’ve got two broad iron sources:
- Animal-based (heme)
- Plant-based (non-heme)
Many people thrive by stacking smart food choices, and then using supplements when diet can’t close the gap. That’s a practical sequence.
In plain English, this means: Heme iron is absorbed 2–3× better than non-heme; pairing plants with vitamin C boosts uptake, while tea/coffee/calcium dampens it.
Iron-rich foods for a natural boost
Here’s a handy snapshot of common foods. Values are typical estimates; actual content varies by brand and preparation.
Pairing plant iron with vitamin C can support absorption, while coffee/tea around meals can reduce it. Make small tweaks; win big.
Food | Serving | Iron (mg) | Bonus Nutrients | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Beef liver | 3 oz (85 g) | ~5–6 | Vitamin A, B12 | Potent but not daily for everyone |
Oysters | 3 oz (85 g) | ~5–8 | Zinc, B12 | High-iron seafood option |
Lean beef | 3 oz (85 g) | ~2 | Protein, B vitamins | Heme iron, well absorbed |
Sardines | 3.75 oz can | ~2–3 | Omega‑3s, calcium | Versatile pantry staple |
Lentils (cooked) | 1/2 cup | ~3 | Folate, fiber | Add vitamin C (citrus, peppers) |
Chickpeas (cooked) | 1/2 cup | ~2 | Fiber, protein | Great in soups and salads |
Tofu (firm) | 1/2 cup | ~3 | Protein, calcium (if set) | Absorption varies |
Spinach (cooked) | 1/2 cup | ~3 | Folate, magnesium | Non‑heme; add vitamin C |
Pumpkin seeds | 1 oz (28 g) | ~2–2.5 | Magnesium, zinc | Easy snack upgrade |
Fortified cereal | 1 serving | ~10–18 | Varies | Check label; can be a top source |
Pairing your food the right way helps: Aim for 50–100 mg vitamin C with iron-rich meals (think citrus or peppers).
Beware strong inhibitors like coffee, tea, and big dairy/calcium around meals—space them out by 1–2 hours. Even cooking tomato sauce in cast-iron pans can add a little extra iron.
Here’s why that matters:
- Vitamin C target: ~50–100 mg with iron-rich meals (citrus, berries, peppers).
- Inhibitors: Coffee/tea, calcium supplements/large dairy, some whole-grain phytates; separate by 1–2 hours.
VitaRx Tip
Cooking acidic foods (tomato sauce) in cast-iron pans can add a small iron boost.
Even great eaters can fall short, especially menstruating and pregnant women, children, and those with absorption issues.
Oral iron is often effective and affordable for uncomplicated cases, while more intensive options (like IV iron) are medical decisions. Personalize with your clinician.
- Many clinicians start 40–65 mg elemental iron every other day (better absorption/tolerance), with vitamin C; avoid taking with calcium/coffee.
- Re-test in ~6–8 weeks; continue 2–3 months after labs normalize to refill stores.
- Pregnant individuals and adult men/postmenopausal women should dose only with clinician guidance.
Product label (common) | Elemental iron (approx.) |
|---|---|
Ferrous sulfate 325 mg | 65 mg |
Ferrous gluconate 325 mg | 36 mg |
Ferrous fumarate 325 mg | 106 mg |
Iron bisglycinate 25 mg | 25 mg (often labeled as elemental) |
Spotlight on VitaRx
At VitaRx, we design for the real world: gentle, effective, transparent. Our iron complex is built to be well-tolerated and mixed, pairing iron with supporting nutrients like vitamin C for absorption and B-vitamins to help cover other common gaps.
We keep formulas minimalist and clean, because your routine needs to work on busy Tuesdays, not just on paper. Simple enough to stick with; strong enough to matter.
Food is your foundation; a smart, gentle supplement fills the cracks. Consistency beats intensity.

Get your personalized vitamin recommendations in less than 3 minutes.
Get your personalized vitamin recommendations in less than 3 minutes.

Expert insights and practical advice
When to check in with a pro: If you or your child develops signs that suggest iron deficiency, especially extreme fatigue, chest discomfort, or breathlessness—see your clinician.
Testing ferritin (storage) and hemoglobin/hematocrit can make the picture clearer; in otherwise healthy adults, a serum ferritin below ~30 mcg/L often suggests iron deficiency, though cutoffs vary by lab and clinical context. Testing is clarity.
Here’s why that matters: Ferritin rises with inflammation—if CRP is elevated or you’re ill, iron deficiency may be present even with ferritin up to ~100 mcg/L; checking transferrin saturation (often <20% in deficiency) helps.
Low hemoglobin and hematocrit are common findings in iron‑deficiency anemia but are not specific to iron deficiency—another reason to include ferritin and transferrin saturation in testing to guide decisions.
Think of it this way:
- Iron deficiency pattern: low ferritin, low transferrin saturation, low MCV/MCH, high RDW.
- If labs don’t fit, your clinician will look for other causes (B12/folate, thyroid, kidney disease).
— Dr. Dimitar Marinov, MD, RDN, PhDIt is important to stress that fatigue and low energy are nonspecific and can result from many other conditions, so iron status should always be confirmed with laboratory tests before starting supplementation. Self-treatment without proper diagnosis may mask underlying causes of blood loss or lead to iron overload, which can be harmful.
Lifestyle that builds results:
- We eat iron-dense meals we actually enjoy, and pair plant iron with vitamin C (citrus, bell peppers). Make it tasty; make it sticky.
- We time our coffee/tea away from iron-rich meals or your supplement. Small timing shift, big upside.
- We train smart—moderate, consistent movement supports energy and mood without overtaxing recovery. Play the long game.
- We track labs with our providers if you’re in a higher-risk group (menstruating women, pregnant individuals, kids, vegetarians/vegans, or those with GI conditions). Data drives better choices.
But wait, how far apart? Remember coffee/tea and calcium supplements 1–2 hours away from iron; acid-reducing meds (PPIs) can lower absorption—ask about timing or IV options if needed.
Also, here’s a quick RDA snapshot for context (varies by age/sex/pregnancy): Adult men ~8 mg/day; women 19–50 ~18 mg/day; pregnancy ~27 mg/day; women 51+ ~8 mg/day. Know your lane.
Age/Sex | Iron RDA (mg/day) |
|---|---|
Children 1–3 yrs | 7 |
Children 4–8 yrs | 10 |
Boys 9–13 yrs | 8 |
Girls 9–13 yrs | 8 |
Boys 14–18 yrs | 11 |
Girls 14–18 yrs | 15 |
Adult men 19–50 yrs | 8 |
Adult women 19–50 yrs | 18 |
Pregnancy (14–50 yrs) | 27 |
Lactation 14–18 yrs | 10 |
Lactation 19–50 yrs | 9 |
Adults 51+ (men and women) | 8 |
Here’s why that matters: the tolerable upper intake level (UL) for adults is 45 mg/day from supplemental and fortified sources (not counting naturally occurring iron) unless supervised; keep all iron products out of children’s reach—overdose can be dangerous.
Test, personalize, and iterate. Your iron plan should fit your life, not the other way around. Sustainable beats extreme.
Comparison: VitaRx vs Other iron supplements
Choosing iron shouldn’t feel like a boss fight. Here’s a clean snapshot to help you decide without getting lost in the weeds. Clarity over noise.
Option | Elemental Iron (typical) | Absorption/Bioavailability | Added Nutrients | Tolerability | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
VitaRx Gentle Iron Complex | Moderate, optimized | Designed for steady uptake | Vitamin C + supportive B‑vitamins | High (gentle on stomach) | Minimalist, transparent formula focus |
Generic Ferrous Sulfate Tablet | 65 mg per 325 mg tab | Well‑studied, can be effective | Usually none | Variable (GI upset common) | Widely used; dosing may need adjustment |
Polysaccharide Iron Complex | Varies | Designed for improved tolerance | Usually none | Often better GI tolerance | Absorption differs by product |
IV Iron (clinic‑only) | N/A | Bypasses gut entirely | Medical setting only | High efficacy under supervision | Reserved for specific clinical cases |
In plain English, this means: Choose the form you can take consistently; evidence supports every-other-day dosing for many people to reduce side effects and improve absorption.
Why choose VitaRx?
- Gentle, effective, consistent—built for taking, not heroics. What you do daily wins.
- Smart match—iron paired with nutrients that play well together. Less friction, more results.
- Quality and transparency—clean labels, research-aligned dosing. Trust comes from clarity.
Here’s why that matters: Some people should avoid unsupervised iron (e.g., hemochromatosis, repeated transfusions, certain thalassemias). Adult men and postmenopausal women should confirm the need with labs.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
Here are some of the most frequently asked questions about iron deficiency.
Final thoughts
Recognizing the symptoms early can make all the difference. Recognizing the symptoms of iron deficiency, unexplained fatigue, pale skin, and shortness of breath, can make a big difference in your health journey.
If you're experiencing these signs, it’s key to explore your options, including dietary shifts and good supplements.
Talk to your healthcare provider about testing your iron levels and consider adding VitaRx Gentle Iron into your routine for better energy levels.
Sources and references
Editor

Derick Rodriguez
Derick Rodriguez focuses on editing health and wellness-related content. With over half a decade of experience in the digital realm, Derick has developed a unique skill set that bridges the gap between complex health concepts and accessible, user-friendly communication. His approach is deeply rooted in leveraging personal experiences and insights to illuminate the nuances of health and wellness topics, making them more approachable and empowering readers with knowledge and confidence.
Fact checker

Dr. Dimitar Marinov
Dr. Marinov has years of experience in scientific research and preventive and clinical medicine. His publications in peer-reviewed journals are on nutritional status, physical activity, and musculoskeletal disorders among adolescents.
At VitaRx, we're not just passionate about our work — we take immense pride in it. Our dedicated team of writers diligently follows strict editorial standards, ensuring that every piece of content we publish is accurate, current, and highly valuable. We don't just strive for quality; we aim for excellence.
Related posts
While you're at it, here are some other relevant articles you might be interested in.

Get your personalized vitamin recommendations in less than
5 minutes.
Get your personalized vitamin recommendations in less than
5 minutes.






